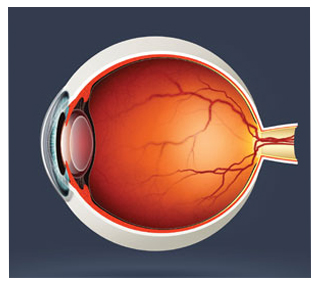
Retinal diseases vary widely, but most of them cause visual symptoms. Retinal diseases can affect any part of your retina, a thin layer of tissue on the inside back wall of your eye.
The retina contains millions of light-sensitive cells (rods and cones) and other nerve cells that receive and organize visual information. Your retina sends this information to your brain through your optic nerve, enabling you to see.
Treatment is available for some retinal diseases. Depending on your condition, treatment goals may be to stop or slow the disease and preserve, improve or restore your vision. Untreated, some retinal diseases can cause severe vision loss or blindness.